Is it closed comedones or fungal acne? A helpful Guide
As someone who has dealt with annoying bumps and blemishes on my skin, I know how frustrating it can be trying to figure out the cause. Is it acne? Clogged pores? A fungal infection? Properly identifying the type of acne is crucial for finding the right treatments to achieve clear, healthy skin.
In this article, I’ll compare two common forms of acne – closed comedones and fungal acne. Understanding the differences between these conditions can help you get to the bottom of your skin woes.
What Exactly Are Closed Comedones?
Contents
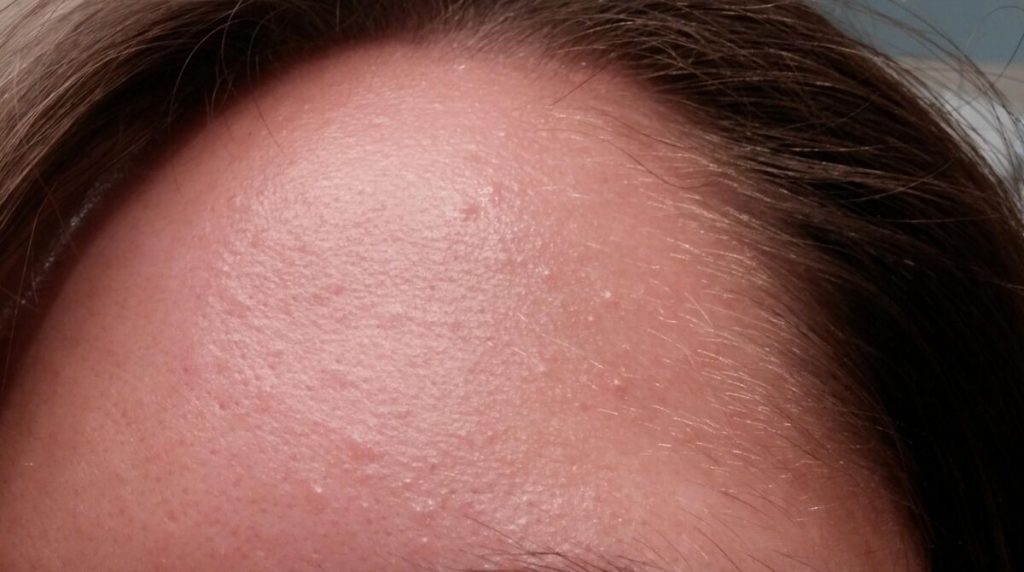
First, let’s cover the basics on closed comedones. These are also referred to as whiteheads and form when pores or hair follicles become clogged with oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria.
The key distinguishing feature of closed comedones compared to blackheads is that the clogged pore remains closed and does not get exposed to air. This stops the trapped contents from oxidizing, resulting in small bumps that are flesh-colored or white.
Common causes leading to closed comedones include:
- Overproduction of sebum and dead skin cells
- Hormonal changes
- Genetics
- Use of comedogenic skincare products
Closed comedones frequently pop up in areas with high concentrations of sebaceous glands. These include the forehead, nose, chin, chest, and back. They appear as uniform, small, and non-inflamed bumps that are painless.
Key Facts About Fungal Acne
Now let’s look at fungal acne, also known as pityrosporum folliculitis or Malassezia folliculitis. As the name suggests, this type of acne is caused by a fungal infection deep within the hair follicles.
The main culprit behind fungal acne is an overgrowth of the yeast Malassezia. When the levels of this fungus grow excessively on the skin’s surface, it leads to irritation and clogged follicles.
Factors contributing to fungal acne include:
- Hot and humid environments
- Excessive sweating
- Skin occlusions caused by tight clothing
- Imbalance in natural skin microbiome due to antibiotics or steroids
This form of acne commonly occurs in adolescents and adult males. However, anyone with increased sweating or frequent skin occlusions may develop fungal acne.
Comparison of Symptoms
Now that we have covered the basics, let’s compare some key characteristics of closed comedones and fungal acne:
Appearance
- Closed comedones – Small, uniform, flesh-colored or white bumps on the skin surface
- Fungal acne – Small red bumps resembling whiteheads, sometimes with a yellowish tinge
Symptoms
- Closed comedones – Are typically not painful or inflamed
- Fungal acne – Can be itchy and may cause a mild burning sensation
Location
- Closed comedones – Most often appear on the face, back, chest
- Fungal acne – Predominantly affects the face, upper back, chest, and shoulders
As you can see, fungal acne and closed comedones share some similarities in where they manifest. However, the appearance and sensations differ.
How to Treat Closed Comedones
When dealing with closed comedones, it’s important to take a multi-pronged approach. Here are some tips:
- Use leave-on salicylic acid treatments to help penetrate pores and dissolve debris
- Try benzoyl peroxide spot treatments to reduce bacteria within pores and quell inflammation
- Incorporate retinoids like adapalene to normalize skin cell turnover and exfoliate
- Cleanse regularly with a gentle cleanser to lift away oil and impurities
- Exfoliate once or twice a week to slough off dead skin cells
- Avoid pore-clogging and comedogenic products
Being consistent with the right topical acne medications while maintaining good cleansing and moisturizing routines is key to treating closed comedones.
Tackling Fungal Acne
When it comes to fungal acne treatment, the approach differs significantly from closed comedones:
- See a dermatologist for proper diagnosis and prescription treatment options
- Avoid using antibiotics and topical steroids, which can make fungal acne worse
- Use anti-dandruff shampoos containing zinc pyrithione or ketoconazole as cleansing agents
- Apply topical antifungal treatments like ketoconazole cream or miconazole
- Oral antifungal medications may be prescribed for moderate to severe cases
- Manage triggers like humidity and sweat to prevent fungal growth and acne flare-ups
As you can see, products that treat regular acne are often ineffective against fungal acne. Seeing a doctor is advised to obtain proper diagnosis and get access to prescription antifungal therapies.
Key Takeaways on Closed Comedones Vs Fungal Acne
Let’s recap some of the main differences between closed comedones and fungal acne:
- Cause – Closed comedones arise from clogged pores, while fungal acne is due to overgrowth of yeast on the skin
- Appearance – Closed comedones manifest as small, flesh-colored bumps vs fungal acne’s red pimple-like bumps
- Symptoms – Closed comedones are not painful, but fungal acne can be itchy and irritating
- Occurrence – Closed comedones are very common, but fungal acne is more prone in adolescents and males
- Treatment – Closed comedones are treated with OTC topical acne meds, while fungal acne requires prescription antifungal treatments
Being able to differentiate between closed comedones and fungal acne is so important for finding the right solutions. Misdiagnosis can lead to frustration and worsened breakouts.
How To Determine If You Have Fungal Acne
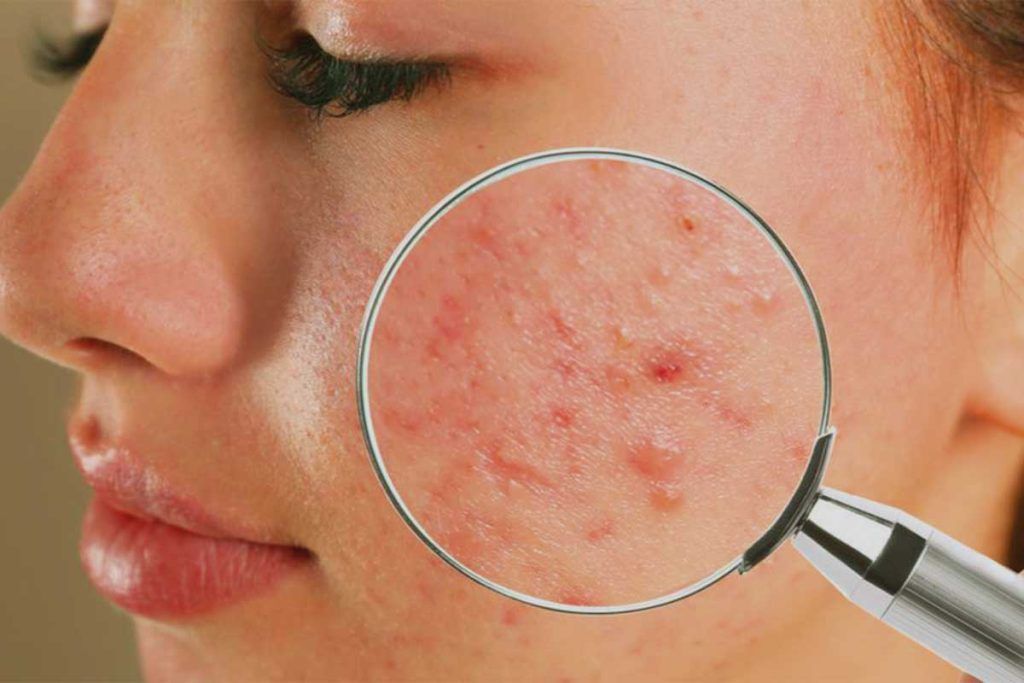
If you suspect you may be dealing with fungal acne, here are a few signs to watch out for:
- Small, uniform bumps concentrated on the forehead, chest, and back
- Mildly itchy or burning sensation when touching affected areas
- Acne that worsens in hot, humid environments or with increased sweating
- Breakouts that persist despite using traditional acne medications
- Recent use of antibiotics or steroids disrupting skin microbiome
Seeing a dermatologist is the best way to get an accurate diagnosis. They can examine your skin more closely and potentially take skin scrapings to check for fungal growth under the microscope.
Tips for Keeping Fungal Acne at Bay
Once fungal acne is under control, be proactive about prevention. Here are some tips:
- Avoid excessive sweating and overheating
- Wear loose, breathable fabrics
- Rinse off after exercise and avoid restrictive workout gear
- Keep skin clean and dry
- Use oil-free skincare products
- Apply dandruff shampoo as a cleansing mask 1-2 times per week
Maintaining a fungal acne-unfriendly environment on your skin is vital for preventing those pesky breakouts from rearing their ugly heads again!
Achieve Your Clearest, Healthiest Skin
I hope this breakdown has helped demystify fungal acne vs closed comedones. While their similarities can make them tough to decipher at first glance, understanding the key differences is empowering.
No one wants to deal with perpetual bumps and blemishes. Seeking professional diagnosis and being consistent with targeted treatment is crucial. With the right knowledge and skincare regimen, you can finally achieve clear skin!

Founded by Sophia Rodriguez, IGXO Cosmetics is a PETA-certified, cruelty-free, and vegan makeup brand.